
Export Credit Refinancing Introduction
In international trade, timing is everything. Exporters often face the challenge of long payment cycles — they ship goods today but may not see payment for 30, 60, or even 120 days. This gap between delivery and payment creates financial pressure, especially for businesses that need working capital to pay suppliers, staff, and fund new orders.
Export credit refinancing offers a solution: by refinancing export receivables, exporters convert pending payments into immediate liquidity. This guide explains how the mechanism works, the benefits and risks, the institutions involved, and practical steps for exporters in 2025.
What is Export Credit Refinancing?
Export credit refinancing is a financial arrangement in which a bank or financial institution advances funds against an export receivable (an invoice). The exporter receives near-term cash while the refinancing institution collects payment from the overseas buyer when the invoice matures.
Refinancing is distinct from pre-shipment financing. The latter funds production and shipment; refinancing occurs after shipment when the invoice exists and payment is due later.
Key Players in the Process
- Exporter: the seller of goods/services.
- Importer/Buyer: the overseas purchaser with deferred payment terms.
- Exporter’s Bank: may provide initial finance or support documentation.
- Refinancing Institution: commercial bank or specialized lender that buys or advances against the receivable.
- Export Credit Agency (ECA): provides guarantees or insurance, reducing non-payment risk (e.g., EXIM, UKEF).
How It Works (Practical Example)
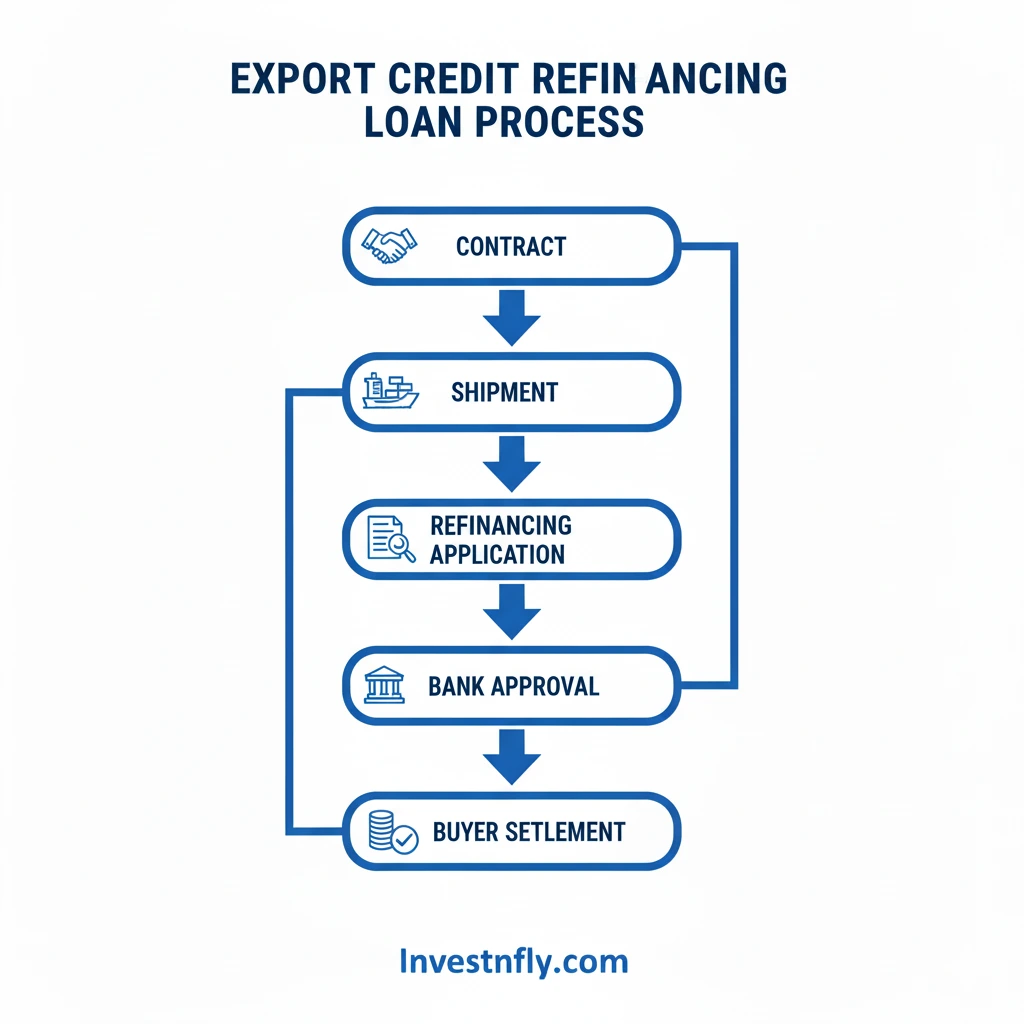
Consider this typical workflow:
- Contract: Exporter (Global Widgets Inc.) sells $1,000,000 of goods to EuroBuys Corp. on 90-day credit.
- Shipment & Invoice: Goods are shipped; an invoice is issued due in 90 days.
- Cash Gap: Global Widgets requires immediate cash to pay suppliers.
- Apply for Refinancing: The exporter applies to its bank or a refinancing institution, submitting the invoice and shipping documents.
- Risk Mitigation: The lender may secure an ECA guarantee or insurance to reduce default risk.
- Advance: The lender advances a percentage of the invoice (commonly 70–95%).
- Collection & Settlement: When the buyer pays, the lender deducts principal, interest and fees; the remainder is returned to the exporter.
This process lets exporters access working capital immediately while the refinancing institution and ECA manage collection risk.
Benefits for Exporters
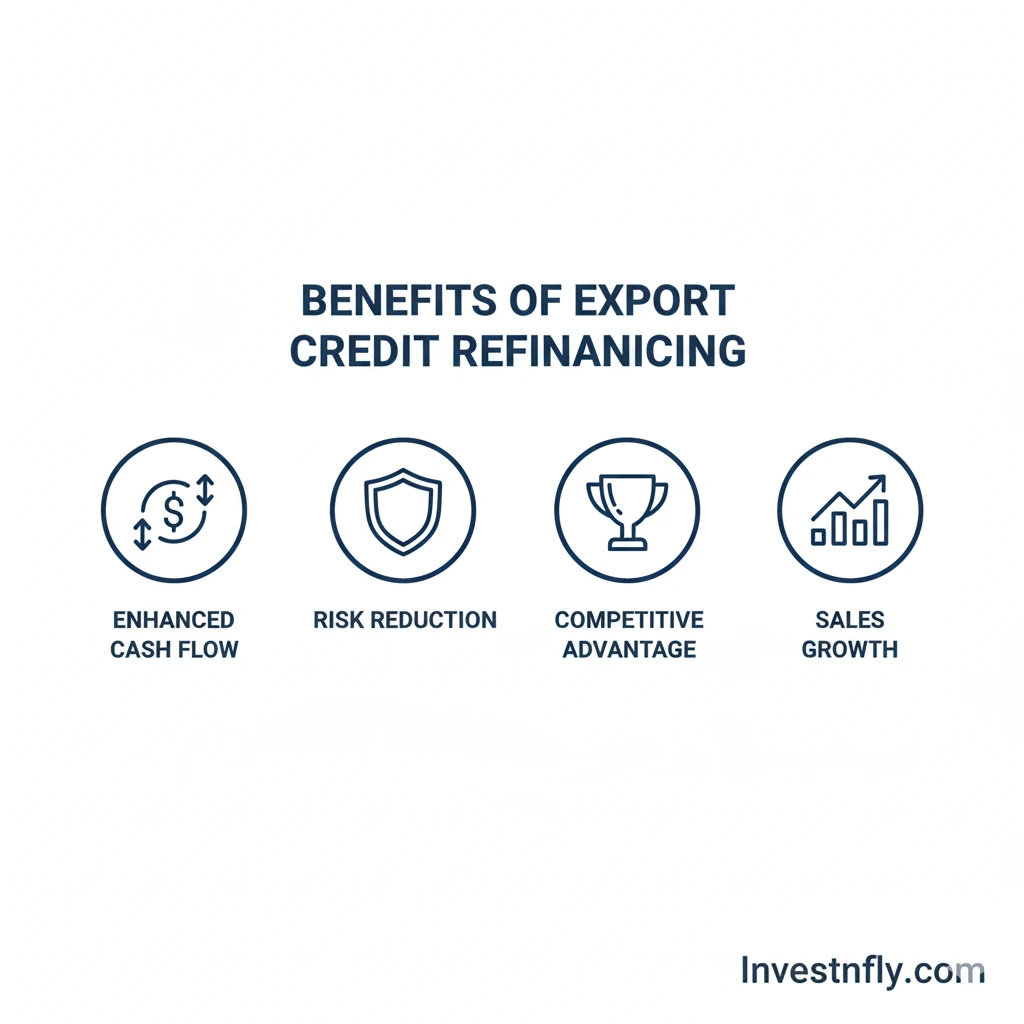
- Improved cash flow: Unlocks funds tied in receivables so you can pay suppliers and reinvest.
- Risk reduction: With an ECA guarantee or insurance, the lender assumes much of the non-payment risk.
- Competitive sales terms: Exporters can offer longer payment terms to customers without straining their own liquidity.
- Scalability: Access to capital enables businesses to accept larger orders and enter new markets.
- Off-balance-sheet options: In some structures receivables are sold outright, improving financial ratios.
Export Credit Refinancing : Drawbacks and Risks
- Cost: Interest and fees reduce net margins; pricing reflects buyer and country risk.
- Complexity: Documentation and legal agreements can be resource-intensive to prepare.
- Recourse exposure: If financing is with recourse, the exporter may remain liable if the importer defaults.
- Eligibility restrictions: Sales to high-risk jurisdictions may not qualify for ECA support.
Eligibility & Requirements for Export Credit Refinancing
Institutions evaluate eligibility based on multiple factors:
- Exporter track record and financial health.
- Importer creditworthiness and payment history.
- Country risk as assessed by ECAs and risk agencies.
- Complete transactional documentation: contract, invoice, bill of lading, insurance or L/C where applicable.
- Nature and origin of the goods—ECA-backed programs often require domestic origin criteria.
Step-by-Step Application Process
- Initial consultation: Contact your bank’s trade finance desk and discuss suitability.
- Document assembly: Gather contracts, invoices, shipping evidence, and buyer information.
- Formal application: Complete the lender’s form and submit documentation.
- Due diligence: Lender assesses buyer, country risk, and transaction structure.
- ECA engagement: If needed, apply for ECA guarantee or insurance.
- Term sheet: If approved, receive terms outlining amount, rate, fees and recourse conditions.
- Legal agreements: Sign the financing and security documents.
- Disbursement: Funds are released; repayment scheduled against the buyer’s eventual payment.
Export Credit Agencies (ECAs) and Their Role
ECAs are pivotal in enabling refinancing by providing guarantees and insurance that make banks willing to finance trade with reduced risk. Notable ECAs include:
- EXIM Bank (United States) — provides loan guarantees and insurance for U.S. exporters.
- UK Export Finance (UKEF) — supports UK exporters through guarantees and direct lending.
- OECD Guidelines — coordinate export credit terms among member countries and provide reporting on official export credit support.
OECD data indicates that official export credit support often exceeds $150 billion annually across member countries, reflecting the scale and importance of trade finance tools like refinancing and guarantees.
Alternatives to Export Credit Refinancing
| Tool | How it works | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Forfaiting | Sale of receivable to a forfaiter on a non-recourse basis | Removes risk, off-balance-sheet | Costlier than refinancing |
| Factoring | Sale of invoices to a factor, often ongoing | Quick liquidity | Can be expensive; suits smaller receivables |
| Letters of Credit (L/C) | Bank guarantees payment if documentary conditions met | High security | Complex and costly |
| Export Working Capital Loan | Short-term loan to fund export operations | Flexible use | Adds debt to the balance sheet |
Frequently Asked Questions
- What’s the difference between Export Financing and Export Credit Refinancing?
Financing supports production before shipment; refinancing converts receivables into cash after shipment.
- Is export credit refinancing costly?
Yes—interest and fees apply. But liquidity gains and risk mitigation often justify the cost for many exporters.
- Can SMEs use export credit refinancing?
Yes. ECAs and some banks provide SME-focused programs to improve access to trade finance.
- How long does approval take?
Generally 2–6 weeks depending on buyer risk, documentation quality, and ECA processing.
- What does non-recourse mean?
Non-recourse financing means the lender cannot pursue the exporter if the buyer defaults; the lender bears the loss.
- Are all countries eligible?
No. Transactions to high-risk or sanctioned countries may be ineligible for ECA-backed refinancing.
- Can I refinance a portion of an invoice?
Yes—partial refinancing is commonly available depending on terms and lender appetite.
- How do exchange rates affect refinancing?
Currency volatility can impact margins; exporters often use hedging strategies like forwards or options.
- Do banks require domestic origin of goods?
Many ECA programs require goods to have domestic origin to qualify for support.
- What documentation is essential?
Export contract, commercial invoice, bill of lading, and any payment security (L/C or insurance) are typically required.
Conclusion
Export credit refinancing is a strategic instrument that helps exporters convert receivables into actionable working capital. While it carries costs and documentation requirements, it reduces payment risk and enables competitive sales terms.
If your business faces long payment cycles and you want to grow internationally without straining cash flow, discuss export credit refinancing with your trade finance advisor and review ECA options that can improve terms and reduce risk.
Related articles:
Further reading & official resources
Trusted sources to learn more about export credit, trade finance and official export credit agencies.
- OECD — Export Credits — Overview of export credit rules, country programs and official guidance.
- World Trade Organization (WTO) — Trade statistics & reports — Global trade data and trend reports useful for export market analysis.
- EXIM Bank (US) — Export-Import Bank of the United States — Official U.S. export credit guarantees, insurance programs and lender resources.
- UK Export Finance (UKEF) — UK government export finance and guarantee services for exporters.
- Investopedia — Trade finance (primer) — Clear, practical explanations of trade finance concepts and instruments.
